Bras Robotisé piloté par nunchuk arduino
De Wikidebrouillard.
Sommaire |
Présentation du projet Arduino
Contrôle d'un bras robotisé par un nunchuk.
On contrôle deux servomoteurs avec un nunchuk, tout cela piloté par la carte arduino.
Liste du matériel
-
 Un Arduino avec son câble USB
Un Arduino avec son câble USB
-
 Un ordinateur
Un ordinateur
-
 Un Nunchuk
Un Nunchuk
-
 Une plaque Labdec
Une plaque Labdec
-
 2 servomoteurs de modélisme
2 servomoteurs de modélisme
-
 Du fil électrique
Du fil électrique
réalisation du projet
Explication
Principe de fonctionnement
Quand on bouge la nunchuk de haut en bas (avec le poignet), le servomoteur qui est collé à la paille se met en action. Quand on bouge la nunchuk sur le même axe (avec le poignet, comme si on vissait), le servomoteur à la base se met à pivoter.
Par défaut, on est en mode accéléromètre. Quand on appui sur la touche C, on passe en mode joystick.
Quand on décale le joystick de gauche à droite, on contrôle le servomoteur qui est à la base. Quand on decale le joystick de haut en bas, on contrôle le servomoteur qui tient la paille.
Quand on appui sur la touche Z, on remet le "robot" en position de départ.
Cablage sur le nunchuk
La photo qui suit nous montre à quoi correspond chaque broche du câble Nunchuck Wii.
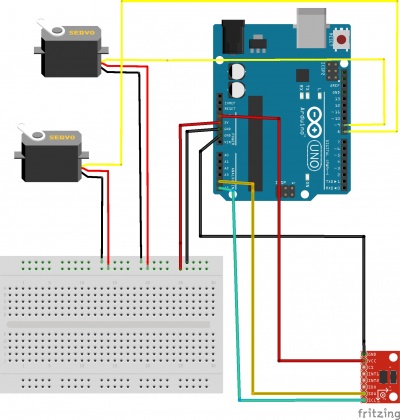
Schéma Fritzing
Code
#include <Wire.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <Servo.h>
// these may need to be adjusted for each nunchuck for calibration
#define ZEROX 510
#define ZEROY 490
#define ZEROZ 460
#define DEFAULT_ZERO_JOY_X 124
#define DEFAULT_ZERO_JOY_Y 132
class WiiChuck {
private:
uint8_t cnt;
uint8_t status[6]; // array to store wiichuck output
uint8_t averageCounter;
int i;
int total;
uint8_t zeroJoyX; // these are about where mine are
uint8_t zeroJoyY; // use calibrateJoy when the stick is at zero to correct
int lastJoyX;
int lastJoyY;
int angles[3];
bool lastZ, lastC;
public:
uint8_t joyX;
uint8_t joyY;
bool buttonZ;
bool buttonC;
void begin()
{
Wire.begin();
cnt = 0;
averageCounter = 0;
// instead of the common 0x40 -> 0x00 initialization, we
// use 0xF0 -> 0x55 followed by 0xFB -> 0x00.
// this lets us use 3rd party nunchucks (like cheap $4 ebay ones)
// while still letting us use official oness.
// only side effect is that we no longer need to decode bytes in _nunchuk_decode_byte
Wire.beginTransmission(0x52); // device address
Wire.write(0xF0);
Wire.write(0x55);
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(1);
Wire.beginTransmission(0x52);
Wire.write(0xFB);
Wire.write(0x01);
Wire.write((uint8_t)0x00);
Wire.endTransmission();
update();
for (i = 0; i<3;i++) {
angles[i] = 0;
}
zeroJoyX = DEFAULT_ZERO_JOY_X;
zeroJoyY = DEFAULT_ZERO_JOY_Y;
}
void calibrateJoy() {
zeroJoyX = joyX;
zeroJoyY = joyY;
}
void update() {
Wire.requestFrom (0x52, 6); // request data from nunchuck
while (Wire.available ()) {
// receive byte as an integer
status[cnt] = _nunchuk_decode_byte (Wire.read()); //
cnt++;
}
if (cnt > 5) {
lastZ = buttonZ;
lastC = buttonC;
lastJoyX = readJoyX();
lastJoyY = readJoyY();
//averageCounter ++;
//if (averageCounter >= AVERAGE_N)
// averageCounter = 0;
cnt = 0;
joyX = (status[0]);
joyY = (status[1]);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
//accelArray[i][averageCounter] = ((int)status[i+2] << 2) + ((status[5] & (B00000011 << ((i+1)*2) ) >> ((i+1)*2)));
angles[i] = (status[i+2] << 2) + ((status[5] & (B00000011 << ((i+1)*2) ) >> ((i+1)*2)));
//accelYArray[averageCounter] = ((int)status[3] << 2) + ((status[5] & B00110000) >> 4);
//accelZArray[averageCounter] = ((int)status[4] << 2) + ((status[5] & B11000000) >> 6);
buttonZ = !( status[5] & B00000001);
buttonC = !((status[5] & B00000010) >> 1);
_send_zero(); // send the request for next bytes
}
}
float readAccelX() {
// total = 0; // accelArray[xyz][averageCounter] * FAST_WEIGHT;
return (float)angles[0] - ZEROX;
}
float readAccelY() {
// total = 0; // accelArray[xyz][averageCounter] * FAST_WEIGHT;
return (float)angles[1] - ZEROY;
}
float readAccelZ() {
// total = 0; // accelArray[xyz][averageCounter] * FAST_WEIGHT;
return (float)angles[2] - ZEROZ;
}
bool zPressed() {
return (buttonZ && ! lastZ);
}
bool cPressed() {
return (buttonC && ! lastC);
}
int readJoyX() {
return (int) joyX - zeroJoyX;
}
int readJoyY() {
return (int)joyY - zeroJoyY;
}
private:
uint8_t _nunchuk_decode_byte (uint8_t x)
{
//decode is only necessary with certain initializations
//x = (x ^ 0x17) + 0x17;
return x;
}
void _send_zero()
{
Wire.beginTransmission (0x52); // transmit to device 0x52
Wire.write ((uint8_t)0x00); // sends one byte
Wire.endTransmission (); // stop transmitting
}
};
WiiChuck chuck = WiiChuck();
Servo servomoteur1, servomoteur2;
int posMoteur1 = 90, posMoteur2 = 90;
int mode=0;
void mode_joystick(int a, int b){
if(a < -50){ // gauche
if(posMoteur1 > 0){
posMoteur1 -= 10;
servomoteur1.write(posMoteur1);
}
}
if(a > 50){ //droite
if(posMoteur1 < 170){
posMoteur1 += 10;
servomoteur1.write(posMoteur1);
}
}
if(b > 50){ //haut
if(posMoteur2 < 180){
posMoteur2 += 10;
servomoteur2.write(posMoteur2);
}
}
if(b < -50){ //bas
if(posMoteur2 > 0){
posMoteur2 -= 10;
servomoteur2.write(posMoteur2);
}
}
}
void mode_accelerometre(int a, int b){
if(a < -50){ // gauche
if(posMoteur1 > 0){
posMoteur1 -= 10;
servomoteur1.write(posMoteur1);
}
}
if(a > 50){ //droite
if(posMoteur1 < 170){
posMoteur1 += 10;
servomoteur1.write(posMoteur1);
}
}
if(b > 50){ //haut
if(posMoteur2 < 180){
posMoteur2 += 10;
servomoteur2.write(posMoteur2);
}
}
if(b < -50){ //bas
if(posMoteur2 > 0){
posMoteur2 -= 10;
servomoteur2.write(posMoteur2);
}
}
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
servomoteur1.attach(8);
servomoteur2.attach(9);
servomoteur1.write(8);
servomoteur2.write(8);
chuck.begin();
}
void loop()
{
chuck.update(); // on actualise les données du nunchuk
if(chuck.zPressed()) // on remet les moteurs à la position de départ
{
posMoteur1 = 90;
posMoteur2 = 90;
servomoteur1.write(posMoteur1);
servomoteur2.write(posMoteur2);
}
if(chuck.cPressed()) // on change le mode
{
if(mode == 1) mode = 0; // on le met en mode joystick
else if(mode == 0) mode = 1; // on le met en mode accelerometre
}
if(mode == 0){ //mode joystick
int a = chuck.readJoyX();
int b = chuck.readJoyY();
mode_joystick(a, b);
}
if(mode == 1){ //mode accelerometre
int x = chuck.readAccelX();
int y = chuck.readAccelY();
mode_accelerometre(x,y);
}
//un petit delai d'attente pour ne pas saturer des servomoteurs
delay(50);
}
Liens avec d'autres projets arduino
chercher ici : http://wikidebrouillard.org/index.php/Catégorie:Arduino
Liens avec le quotidien
On pourrait controler plein de chose avec le nunchuk comme google earth ou encore le curseur de votre ordinateur.