Allumage d'une led avec un RFID Shield
De Wikidebrouillard.
(→Présentation du projet Arduino) |
(→Schéma Fritzing) |
||
| (20 versions intermédiaires masquées) | |||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
{{avertissement}} | {{avertissement}} | ||
| - | {{vidéo|numérovidéo = <videoflash type="mediaspip" num ="1">http://mediaspip.ptitdeb.infini.fr/IMG/ | + | {{vidéo|numérovidéo = <videoflash type="mediaspip" num ="1">http://mediaspip.ptitdeb.infini.fr/IMG/flv/arduino.flv|400|300</videoflash>}} |
| - | ==Présentation du projet Arduino== | + | ==Présentation du projet Arduino==Le NFC permet d'utiliser des cartes magnétiques pour réaliser divers actions comme ouvrir une porte, effectuer un paiement,etc. |
| + | Donc on va utiliser ces cartes pour allumer une led, ici on prendra une led RGB qui permet de faire plusieurs couleurs avec un composant. | ||
| - | Le NFC permet d'utiliser des cartes magnétiques pour réaliser divers actions comme ouvrir une porte, effectuer un paiement, | + | ==Présentation du projet Arduino== |
| + | Le NFC permet d'utiliser des cartes magnétiques pour réaliser divers actions comme ouvrir une porte, effectuer un paiement,etc. | ||
Donc on va utiliser ces cartes pour allumer une led, ici on prendra une led RGB qui permet de faire plusieurs couleurs avec un composant. | Donc on va utiliser ces cartes pour allumer une led, ici on prendra une led RGB qui permet de faire plusieurs couleurs avec un composant. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
==réalisation du projet== | ==réalisation du projet== | ||
===Explication=== | ===Explication=== | ||
| + | Voici quelques points à vérifier avant d'entamer le tuto. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | La LED RGB | ||
| + | |||
| + | il existe deux types | ||
| + | - '''cathode commune''', il y a une broche de masse et les trois autres | ||
| + | servent d'alimentations propre à chaque couleur | ||
| + | - '''anode commune''', il y a une broche d'alimentation | ||
| + | |||
| + | Il est important de connaitre le type, car cela impact le code. | ||
| + | Exemple pour une anode commune, pour éteindre la led, il faut que la patte de contrôle soit à l'état haut, et bas pour l'éteindre. La logique est inverse pour une cathode commune. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Le shield RFID | ||
| + | |||
| + | Il est livré avec des connecteurs mâles, à prendre en compte car les cotes empêchent de connecter le shield sur une breadboard | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Le code | ||
| + | |||
| + | Il est important de faire attention à la manière d'écrire. | ||
| + | Surtout pour les noms de variables. | ||
| + | Exemple: variable n'est pas la même chose que Variable | ||
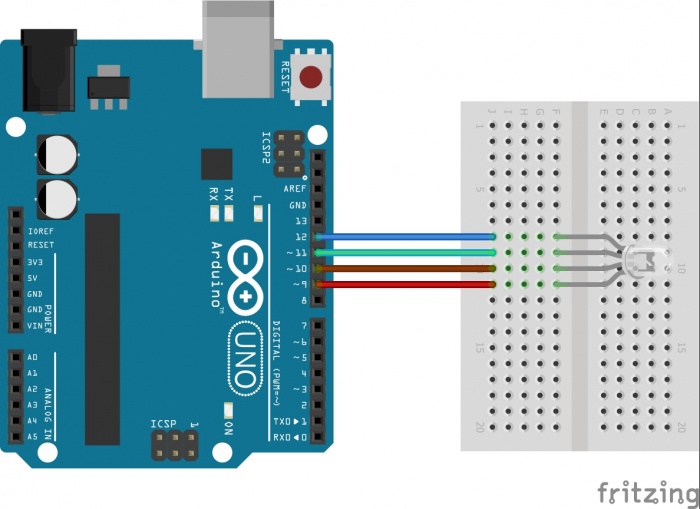
===Schéma Fritzing=== | ===Schéma Fritzing=== | ||
| + | [[Fichier:Schema fritzing.jpg|700px]] | ||
===Code=== | ===Code=== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| + | /**************************************************************************/ | ||
| + | /*! | ||
| + | @file iso14443a_uid.pde | ||
| + | @author Adafruit Industries | ||
| + | @license BSD (see license.txt) | ||
| + | |||
| + | This example will attempt to connect to an ISO14443A | ||
| + | card or tag and retrieve some basic information about it | ||
| + | that can be used to determine what type of card it is. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that you need the baud rate to be 115200 because we need to print | ||
| + | out the data and read from the card at the same time! | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is an example sketch for the Adafruit PN532 NFC/RFID breakout boards | ||
| + | This library works with the Adafruit NFC breakout | ||
| + | ----> https://www.adafruit.com/products/364 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check out the links above for our tutorials and wiring diagrams | ||
| + | These chips use I2C to communicate, 4 pins required to interface: | ||
| + | SDA (I2C Data) and SCL (I2C Clock), IRQ and RESET (any digital line) | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | /**************************************************************************/ | ||
#include <Wire.h> | #include <Wire.h> | ||
#include <Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C.h> | #include <Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C.h> | ||
| Ligne 32 : | Ligne 72 : | ||
Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C nfc(IRQ, RESET); | Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C nfc(IRQ, RESET); | ||
| + | |||
| + | //****************** Definition des sorties de L'arduino ************************* | ||
int ledR = 9; | int ledR = 9; | ||
int ledP = 10; | int ledP = 10; | ||
int ledG = 11; | int ledG = 11; | ||
int ledB = 12; | int ledB = 12; | ||
| + | |||
| + | //********************* Identifiants des clés valides ***************************** | ||
uint8_t comp01[] = { 203,102,125,189,0,0,0 }; | uint8_t comp01[] = { 203,102,125,189,0,0,0 }; | ||
uint8_t comp02[] = { 77,243,159,35,0,0,0 }; | uint8_t comp02[] = { 77,243,159,35,0,0,0 }; | ||
uint8_t comp03[] = { 45,187,161,35,0,0,0 }; | uint8_t comp03[] = { 45,187,161,35,0,0,0 }; | ||
| - | //***************** | + | //*****************Initilisation des sorties de l'Arduino**************************** |
void setup(void) { | void setup(void) { | ||
Serial.begin(115200); | Serial.begin(115200); | ||
| Ligne 57 : | Ligne 101 : | ||
if (! versiondata) { | if (! versiondata) { | ||
Serial.print("Didn't find PN53x board"); | Serial.print("Didn't find PN53x board"); | ||
| - | while (1); // | + | while (1); // arret |
} | } | ||
| - | // | + | // SI les données sont OK, le programme l'affiche dans la console |
Serial.print("Found chip PN5"); Serial.println((versiondata>>24) & 0xFF, HEX); | Serial.print("Found chip PN5"); Serial.println((versiondata>>24) & 0xFF, HEX); | ||
Serial.print("Firmware ver. "); Serial.print((versiondata>>16) & 0xFF, DEC); | Serial.print("Firmware ver. "); Serial.print((versiondata>>16) & 0xFF, DEC); | ||
| Ligne 70 : | Ligne 114 : | ||
nfc.setPassiveActivationRetries(0xFF); | nfc.setPassiveActivationRetries(0xFF); | ||
| - | // configure | + | // configure la carte pour lire le NFC |
nfc.SAMConfig(); | nfc.SAMConfig(); | ||
| Ligne 77 : | Ligne 121 : | ||
| - | //***********************************Boucle | + | //***********************************Boucle Principale ********************* |
| + | //************************************************************************** | ||
void loop(void) { | void loop(void) { | ||
int count = 0; | int count = 0; | ||
boolean success; | boolean success; | ||
| - | uint8_t uid[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // | + | uint8_t uid[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // Variable permettant de stocker temporairement la valeur de l'identifiant de la carte |
| - | uint8_t uidLength; // | + | uint8_t uidLength; // Longueur de l'identifiant (4 or 7 bites, generalement 4 pour les cartes livrées avec) |
| - | // | + | // Attend pour une carte ISO14443A (Mifare, etc.). Quand une est trouvée |
| - | // 'uid' | + | // 'uid' sera remplie avec l'identifiant de la carte, and uidLength indiquera |
| - | // | + | // si uid fait 4 bites (Mifare Classic) ou 7 bites (Mifare Ultralight) |
success = nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, &uid[0], &uidLength); | success = nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, &uid[0], &uidLength); | ||
| Ligne 95 : | Ligne 140 : | ||
| - | //*******************Affichage INFO Carte***************************** | + | //*************************Affichage INFO Carte ********************************* |
Serial.print("UID Value: "); | Serial.print("UID Value: "); | ||
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | ||
| Ligne 108 : | Ligne 153 : | ||
} | } | ||
| - | //******************Comparaison Clé | + | //******************Comparaison Clé valide 1************************** |
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | ||
{ | { | ||
| Ligne 122 : | Ligne 167 : | ||
} | } | ||
| - | //*********************Comparaison Clé | + | //*********************Comparaison Clé valide 2************************* |
count=0; | count=0; | ||
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | ||
| Ligne 137 : | Ligne 182 : | ||
} | } | ||
| - | //*********************Comparaison Clé | + | //*********************Comparaison Clé valide 3************************* |
count=0; | count=0; | ||
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | ||
| Ligne 150 : | Ligne 195 : | ||
digitalWrite(ledG, LOW); | digitalWrite(ledG, LOW); | ||
digitalWrite(ledB, HIGH); | digitalWrite(ledB, HIGH); | ||
| - | } | + | } |
| - | + | } | |
| - | + | ||
| - | //****************************Carte Magnetique Imcompatible***************** | + | //*******************Comparaison Clé Valide 4**************************** |
| - | + | ||
| + | //A definir | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | //****************************Carte Magnetique Imcompatible***************** | ||
else | else | ||
{ | { | ||
| - | // PN532 | + | // PN532 Patiente jusqu'a la prochaine carte |
Serial.println("Timed out waiting for a card"); | Serial.println("Timed out waiting for a card"); | ||
} | } | ||
| - | delay(1500); | + | delay(1500);//rèle la durée entre deux cycles d'acquisition (en millisecondes) |
} | } | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| - | == | + | ===code=== |
| - | + | /**************************************************************************/ | |
| + | /*! | ||
| + | @file iso14443a_uid.pde | ||
| + | @author Adafruit Industries | ||
| + | @license BSD (see license.txt) | ||
| - | == | + | This example will attempt to connect to an ISO14443A |
| + | card or tag and retrieve some basic information about it | ||
| + | that can be used to determine what type of card it is. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that you need the baud rate to be 115200 because we need to print | ||
| + | out the data and read from the card at the same time! | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check out the links above for our tutorials and wiring diagrams | ||
| + | These chips use I2C to communicate, 4 pins required to interface: | ||
| + | SDA (I2C Data) and SCL (I2C Clock), IRQ and RESET (any digital line) | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | /**************************************************************************/ | ||
| + | #include <Wire.h> | ||
| + | #include <Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C.h> | ||
| + | |||
| + | #define IRQ (2) | ||
| + | #define RESET (3) // Not connected by default on the NFC Shield | ||
| + | |||
| + | Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C nfc(IRQ, RESET); | ||
| + | |||
| + | //****************** Definition des sorties de L'arduino ************************* | ||
| + | int ledR = 9; | ||
| + | int ledP = 10; | ||
| + | int ledG = 11; | ||
| + | int ledB = 12; | ||
| + | |||
| + | //********************* Identifiants des clés valides ***************************** | ||
| + | uint8_t comp01[] = { 203,102,125,189,0,0,0 }; | ||
| + | uint8_t comp02[] = { 77,243,159,35,0,0,0 }; | ||
| + | uint8_t comp03[] = { 45,187,161,35,0,0,0 }; | ||
| + | |||
| + | //*****************Initilisation des sorties de l'Arduino**************************** | ||
| + | void setup(void) { | ||
| + | Serial.begin(115200); | ||
| + | Serial.println("Hello!"); | ||
| + | pinMode(ledP, OUTPUT); | ||
| + | pinMode(ledR, OUTPUT); | ||
| + | pinMode(ledG, OUTPUT); | ||
| + | pinMode(ledB, OUTPUT); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledR,HIGH); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledB,HIGH); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledG,HIGH); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledP,HIGH); | ||
| + | nfc.begin(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | uint32_t versiondata = nfc.getFirmwareVersion(); | ||
| + | if (! versiondata) { | ||
| + | Serial.print("Didn't find PN53x board"); | ||
| + | while (1); // arret | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // SI les données sont OK, le programme l'affiche dans la console | ||
| + | Serial.print("Found chip PN5"); Serial.println((versiondata>>24) & 0xFF, HEX); | ||
| + | Serial.print("Firmware ver. "); Serial.print((versiondata>>16) & 0xFF, DEC); | ||
| + | Serial.print('.'); Serial.println((versiondata>>8) & 0xFF, DEC); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Set the max number of retry attempts to read from a card | ||
| + | // This prevents us from waiting forever for a card, which is | ||
| + | // the default behaviour of the PN532. | ||
| + | nfc.setPassiveActivationRetries(0xFF); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // configure la carte pour lire le NFC | ||
| + | nfc.SAMConfig(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serial.println("Waiting for an ISO14443A card"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | //***********************************Boucle Principale ********************* | ||
| + | //************************************************************************** | ||
| + | void loop(void) { | ||
| + | int count = 0; | ||
| + | boolean success; | ||
| + | uint8_t uid[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // Variable permettant de stocker temporairement la valeur de l'identifiant de la carte | ||
| + | uint8_t uidLength; // Longueur de l'identifiant (4 or 7 bites, generalement 4 pour les cartes livrées avec) | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Attend pour une carte ISO14443A (Mifare, etc.). Quand une est trouvée | ||
| + | // 'uid' sera remplie avec l'identifiant de la carte, and uidLength indiquera | ||
| + | // si uid fait 4 bites (Mifare Classic) ou 7 bites (Mifare Ultralight) | ||
| + | success = nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, &uid[0], &uidLength); | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (success) { | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serial.println("Found a card!"); | ||
| + | Serial.print("UID Length: ");Serial.print(uidLength, DEC);Serial.println(" bytes"); | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | //*************************Affichage INFO Carte ********************************* | ||
| + | Serial.print("UID Value: "); | ||
| + | for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | Serial.print(" ");Serial.print(uid[i], DEC); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | Serial.println(""); | ||
| + | Serial.print("UID Value: "); | ||
| + | for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | Serial.print(" ");Serial.print(uid[i], HEX); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | //******************Comparaison Clé valide 1************************** | ||
| + | for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | if (uid[i]==comp01[i]){ | ||
| + | count=count + 1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (count==uidLength){ | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledR, LOW); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledG, HIGH); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledB, HIGH); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | //*********************Comparaison Clé valide 2************************* | ||
| + | count=0; | ||
| + | for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | if (uid[i]==comp02[i]){ | ||
| + | count=count + 1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (count==uidLength){ | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledR, HIGH); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledG, HIGH); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledB, LOW); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | //*********************Comparaison Clé valide 3************************* | ||
| + | count=0; | ||
| + | for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | if (uid[i]==comp03[i]){ | ||
| + | count=count + 1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (count==uidLength){ | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledR, HIGH); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledG, LOW); | ||
| + | digitalWrite(ledB, HIGH); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | //*******************Comparaison Clé Valide 4**************************** | ||
| + | |||
| + | //A definir | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | //****************************Carte Magnetique Imcompatible***************** | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | // PN532 Patiente jusqu'a la prochaine carte | ||
| + | Serial.println("Timed out waiting for a card"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | delay(1500);//rèle la durée entre deux cycles d'acquisition (en millisecondes) | ||
| + | } | ||
==Liens avec le quotidien== | ==Liens avec le quotidien== | ||
| - | + | Actuellement le NFC se trouve déjà dans les smartphones, cartes | |
| + | bancaires, passe d'identification. A l'avenir on pourra surement | ||
| + | démarrer sa voiture avec, allumer la lumière chez soi, etc. | ||
[[Catégorie:Arduino]] | [[Catégorie:Arduino]] | ||
Version actuelle en date du 26 janvier 2014 à 02:28
==Présentation du projet Arduino==Le NFC permet d'utiliser des cartes magnétiques pour réaliser divers actions comme ouvrir une porte, effectuer un paiement,etc.
Donc on va utiliser ces cartes pour allumer une led, ici on prendra une led RGB qui permet de faire plusieurs couleurs avec un composant.
Sommaire |
Présentation du projet Arduino
Le NFC permet d'utiliser des cartes magnétiques pour réaliser divers actions comme ouvrir une porte, effectuer un paiement,etc.
Donc on va utiliser ces cartes pour allumer une led, ici on prendra une led RGB qui permet de faire plusieurs couleurs avec un composant.
réalisation du projet
Explication
Voici quelques points à vérifier avant d'entamer le tuto.
La LED RGB
il existe deux types
- cathode commune, il y a une broche de masse et les trois autres servent d'alimentations propre à chaque couleur - anode commune, il y a une broche d'alimentation
Il est important de connaitre le type, car cela impact le code. Exemple pour une anode commune, pour éteindre la led, il faut que la patte de contrôle soit à l'état haut, et bas pour l'éteindre. La logique est inverse pour une cathode commune.
Le shield RFID
Il est livré avec des connecteurs mâles, à prendre en compte car les cotes empêchent de connecter le shield sur une breadboard
Le code
Il est important de faire attention à la manière d'écrire. Surtout pour les noms de variables. Exemple: variable n'est pas la même chose que Variable
Schéma Fritzing
Code
/**************************************************************************/
/*!
@file iso14443a_uid.pde
@author Adafruit Industries
@license BSD (see license.txt)
This example will attempt to connect to an ISO14443A
card or tag and retrieve some basic information about it
that can be used to determine what type of card it is.
Note that you need the baud rate to be 115200 because we need to print
out the data and read from the card at the same time!
This is an example sketch for the Adafruit PN532 NFC/RFID breakout boards
This library works with the Adafruit NFC breakout
----> https://www.adafruit.com/products/364
Check out the links above for our tutorials and wiring diagrams
These chips use I2C to communicate, 4 pins required to interface:
SDA (I2C Data) and SCL (I2C Clock), IRQ and RESET (any digital line)
*/
/**************************************************************************/
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C.h>
#define IRQ (2)
#define RESET (3) // Not connected by default on the NFC Shield
Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C nfc(IRQ, RESET);
//****************** Definition des sorties de L'arduino *************************
int ledR = 9;
int ledP = 10;
int ledG = 11;
int ledB = 12;
//********************* Identifiants des clés valides *****************************
uint8_t comp01[] = { 203,102,125,189,0,0,0 };
uint8_t comp02[] = { 77,243,159,35,0,0,0 };
uint8_t comp03[] = { 45,187,161,35,0,0,0 };
//*****************Initilisation des sorties de l'Arduino****************************
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Hello!");
pinMode(ledP, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledG, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledB, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(ledR,HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledB,HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledG,HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledP,HIGH);
nfc.begin();
uint32_t versiondata = nfc.getFirmwareVersion();
if (! versiondata) {
Serial.print("Didn't find PN53x board");
while (1); // arret
}
// SI les données sont OK, le programme l'affiche dans la console
Serial.print("Found chip PN5"); Serial.println((versiondata>>24) & 0xFF, HEX);
Serial.print("Firmware ver. "); Serial.print((versiondata>>16) & 0xFF, DEC);
Serial.print('.'); Serial.println((versiondata>>8) & 0xFF, DEC);
// Set the max number of retry attempts to read from a card
// This prevents us from waiting forever for a card, which is
// the default behaviour of the PN532.
nfc.setPassiveActivationRetries(0xFF);
// configure la carte pour lire le NFC
nfc.SAMConfig();
Serial.println("Waiting for an ISO14443A card");
}
//***********************************Boucle Principale *********************
//**************************************************************************
void loop(void) {
int count = 0;
boolean success;
uint8_t uid[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // Variable permettant de stocker temporairement la valeur de l'identifiant de la carte
uint8_t uidLength; // Longueur de l'identifiant (4 or 7 bites, generalement 4 pour les cartes livrées avec)
// Attend pour une carte ISO14443A (Mifare, etc.). Quand une est trouvée
// 'uid' sera remplie avec l'identifiant de la carte, and uidLength indiquera
// si uid fait 4 bites (Mifare Classic) ou 7 bites (Mifare Ultralight)
success = nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, &uid[0], &uidLength);
if (success) {
Serial.println("Found a card!");
Serial.print("UID Length: ");Serial.print(uidLength, DEC);Serial.println(" bytes");
//*************************Affichage INFO Carte *********************************
Serial.print("UID Value: ");
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
Serial.print(" ");Serial.print(uid[i], DEC);
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("UID Value: ");
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
Serial.print(" ");Serial.print(uid[i], HEX);
}
//******************Comparaison Clé valide 1**************************
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
if (uid[i]==comp01[i]){
count=count + 1;
}
}
if (count==uidLength){
digitalWrite(ledR, LOW);
digitalWrite(ledG, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledB, HIGH);
}
//*********************Comparaison Clé valide 2*************************
count=0;
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
if (uid[i]==comp02[i]){
count=count + 1;
}
}
if (count==uidLength){
digitalWrite(ledR, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledG, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledB, LOW);
}
//*********************Comparaison Clé valide 3*************************
count=0;
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
if (uid[i]==comp03[i]){
count=count + 1;
}
}
if (count==uidLength){
digitalWrite(ledR, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledG, LOW);
digitalWrite(ledB, HIGH);
}
}
//*******************Comparaison Clé Valide 4****************************
//A definir
//****************************Carte Magnetique Imcompatible*****************
else
{
// PN532 Patiente jusqu'a la prochaine carte
Serial.println("Timed out waiting for a card");
}
delay(1500);//rèle la durée entre deux cycles d'acquisition (en millisecondes)
}
code
/**************************************************************************/ /*!
@file iso14443a_uid.pde @author Adafruit Industries @license BSD (see license.txt)
This example will attempt to connect to an ISO14443A card or tag and retrieve some basic information about it that can be used to determine what type of card it is. Note that you need the baud rate to be 115200 because we need to print out the data and read from the card at the same time!
Check out the links above for our tutorials and wiring diagrams These chips use I2C to communicate, 4 pins required to interface: SDA (I2C Data) and SCL (I2C Clock), IRQ and RESET (any digital line)
- /
/**************************************************************************/
- include <Wire.h>
- include <Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C.h>
- define IRQ (2)
- define RESET (3) // Not connected by default on the NFC Shield
Adafruit_NFCShield_I2C nfc(IRQ, RESET);
//****************** Definition des sorties de L'arduino *************************
int ledR = 9;
int ledP = 10;
int ledG = 11;
int ledB = 12;
//********************* Identifiants des clés valides *****************************
uint8_t comp01[] = { 203,102,125,189,0,0,0 };
uint8_t comp02[] = { 77,243,159,35,0,0,0 };
uint8_t comp03[] = { 45,187,161,35,0,0,0 };
//*****************Initilisation des sorties de l'Arduino**************************** void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Hello!");
pinMode(ledP, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledG, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledB, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(ledR,HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledB,HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledG,HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledP,HIGH);
nfc.begin();
uint32_t versiondata = nfc.getFirmwareVersion();
if (! versiondata) {
Serial.print("Didn't find PN53x board");
while (1); // arret
}
// SI les données sont OK, le programme l'affiche dans la console
Serial.print("Found chip PN5"); Serial.println((versiondata>>24) & 0xFF, HEX);
Serial.print("Firmware ver. "); Serial.print((versiondata>>16) & 0xFF, DEC);
Serial.print('.'); Serial.println((versiondata>>8) & 0xFF, DEC);
// Set the max number of retry attempts to read from a card
// This prevents us from waiting forever for a card, which is
// the default behaviour of the PN532.
nfc.setPassiveActivationRetries(0xFF);
// configure la carte pour lire le NFC
nfc.SAMConfig();
Serial.println("Waiting for an ISO14443A card");
}
//***********************************Boucle Principale *********************
//**************************************************************************
void loop(void) {
int count = 0;
boolean success;
uint8_t uid[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // Variable permettant de stocker temporairement la valeur de l'identifiant de la carte
uint8_t uidLength; // Longueur de l'identifiant (4 or 7 bites, generalement 4 pour les cartes livrées avec)
// Attend pour une carte ISO14443A (Mifare, etc.). Quand une est trouvée
// 'uid' sera remplie avec l'identifiant de la carte, and uidLength indiquera
// si uid fait 4 bites (Mifare Classic) ou 7 bites (Mifare Ultralight)
success = nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, &uid[0], &uidLength);
if (success) {
Serial.println("Found a card!");
Serial.print("UID Length: ");Serial.print(uidLength, DEC);Serial.println(" bytes");
//*************************Affichage INFO Carte *********************************
Serial.print("UID Value: ");
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
Serial.print(" ");Serial.print(uid[i], DEC);
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("UID Value: ");
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
Serial.print(" ");Serial.print(uid[i], HEX);
}
//******************Comparaison Clé valide 1**************************
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
if (uid[i]==comp01[i]){
count=count + 1;
}
}
if (count==uidLength){
digitalWrite(ledR, LOW);
digitalWrite(ledG, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledB, HIGH);
}
//*********************Comparaison Clé valide 2*************************
count=0;
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
if (uid[i]==comp02[i]){
count=count + 1;
}
}
if (count==uidLength){
digitalWrite(ledR, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledG, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledB, LOW);
}
//*********************Comparaison Clé valide 3*************************
count=0;
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
if (uid[i]==comp03[i]){
count=count + 1;
}
}
if (count==uidLength){
digitalWrite(ledR, HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledG, LOW);
digitalWrite(ledB, HIGH);
}
}
//*******************Comparaison Clé Valide 4****************************
//A definir
//****************************Carte Magnetique Imcompatible*****************
else
{
// PN532 Patiente jusqu'a la prochaine carte
Serial.println("Timed out waiting for a card");
}
delay(1500);//rèle la durée entre deux cycles d'acquisition (en millisecondes)
}
Liens avec le quotidien
Actuellement le NFC se trouve déjà dans les smartphones, cartes bancaires, passe d'identification. A l'avenir on pourra surement démarrer sa voiture avec, allumer la lumière chez soi, etc.
- Dernière modification de cette page le 26 janvier 2014 à 02:28.
- Cette page a été consultée 52 638 fois.
- Contenu disponible sous Creative Commons - Paternite Partage a l'identique (CC-BY-SA).
- Politique de confidentialité
- À propos de Wikidebrouillard
- Avertissements